Dyson, the U.K. company famous for its bagless vacuum cleaners, has acquired Michigan-based solid-state battery startup Sakti3 for $90 million and announced plans to build an important $1 billion battery factory to mass produce the next generation battery technology.
This is the second important solid-state battery technology acquisition in a short period of time – Bosch recently bought Seeo Inc. to bring their battery technology to market. Solid-state batteries are thought to be a lot safer than common li-ion cells and could have more potential for higher energy density, but we have yet to see a company capable of producing it in large-scale and at an attractive price point.
Sakti3 made the headlines last year when it announced that it had produced a solid-state battery cell with 400 Wh/kg energy density, compared to Tesla’s cells believed to be around 230 Wh/kg.
Dyson had already invested $15 million in Sakti3 before now buying the company.
Founder and CEO Ann Marie Sastry will join Dyson as an executive and lead development of her battery technology for the company. When she first unveiled her technology and was trying to attract investors, Sastry said that the company’s solid-state cells aimed at the electric vehicle industry.
Dyson says that they remain open at licensing the technology and the cells could eventually find their way into electric cars, but for now the plan is to integrate the technology into Dyson’s cordless vacuum cleaners. The company expects to start producing its systems with the new batteries within a year or two.
“If we are to continue to create new and disruptive technology we must develop more advanced core technologies,” said Dyson founder James Dyson. “We have invested nearly $310 million into the research and development of the Dyson digital motor, a technology that now powers our most successful machines. We will do the same with batteries. Sakti3 has developed a breakthrough in battery technology, and together we will make this technology a reality.”

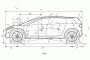 Dyson, the maker of snazzy, high-tech vacuum cleaners, has said for two years that it will build electric cars starting in 2020. Now the company has released patent drawings that give a hint of what at least the first one may look like. READ THIS: Dyson plans to build its electric car in Singapore The drawings show a long, low crossover...
Dyson, the maker of snazzy, high-tech vacuum cleaners, has said for two years that it will build electric cars starting in 2020. Now the company has released patent drawings that give a hint of what at least the first one may look like. READ THIS: Dyson plans to build its electric car in Singapore The drawings show a long, low crossover...  Dyson, the maker of snazzy, high-tech vacuum cleaners, has said for two years that it will build electric cars starting in 2020. Now the company has released patent drawings that give a hint of what at least the first one may look like. READ THIS: Dyson plans to build its electric car in Singapore The drawings show a long, low crossover...
Dyson, the maker of snazzy, high-tech vacuum cleaners, has said for two years that it will build electric cars starting in 2020. Now the company has released patent drawings that give a hint of what at least the first one may look like. READ THIS: Dyson plans to build its electric car in Singapore The drawings show a long, low crossover... 

 Americans are taking climate change more seriously, and a majority think the government should do something about it, two new studies show. A startup company thinks it has a software hack to help electric-car batteries charge faster. And Nissan's Carlos Ghosn has resigned as Chairman and CEO of Renault. All this and more on Green Car Reports. In a...
Americans are taking climate change more seriously, and a majority think the government should do something about it, two new studies show. A startup company thinks it has a software hack to help electric-car batteries charge faster. And Nissan's Carlos Ghosn has resigned as Chairman and CEO of Renault. All this and more on Green Car Reports. In a... 
 Dyson, famous for reinventing vacuum cleaners, looks to be getting serious about building electric cars. The company announced on Tuesday it has hired former Infiniti President Roland Krueger to head its automotive operations. Under Krueger's tenure, Infiniti, Nissan's luxury brand, announced that it would convert most of its models to electric or...
Dyson, famous for reinventing vacuum cleaners, looks to be getting serious about building electric cars. The company announced on Tuesday it has hired former Infiniti President Roland Krueger to head its automotive operations. Under Krueger's tenure, Infiniti, Nissan's luxury brand, announced that it would convert most of its models to electric or... 
 Dyson, the British maker of premium vacuum cleaners, aims to enter the electric-car arena—and it’s chosen Singapore as the global assembly site. The company confirmed that its board has ratified the decision for the company itself to construct what it calls a “purpose-built advanced automotive manufacturing facility” there...
Dyson, the British maker of premium vacuum cleaners, aims to enter the electric-car arena—and it’s chosen Singapore as the global assembly site. The company confirmed that its board has ratified the decision for the company itself to construct what it calls a “purpose-built advanced automotive manufacturing facility” there... 
 In another step to show it's serious about building an electric car, Dyson, the British vacuum-cleaner maker, has laid out plans to build a test track in Britain. Reuters reported Thursday that Dyson plans to build a vehicle test track at a former World War II airfield in Wiltshire, England, to go along with previously announced plans for an...
In another step to show it's serious about building an electric car, Dyson, the British vacuum-cleaner maker, has laid out plans to build a test track in Britain. Reuters reported Thursday that Dyson plans to build a vehicle test track at a former World War II airfield in Wiltshire, England, to go along with previously announced plans for an... 
![James Dyson with digital motors [image: Dyson]](https://images.hgmsites.net/tmb/james-dyson-with-digital-motors-image-dyson_100531077_t.gif) While Dyson may be best known worldwide for high-tech vacuum cleaners, the company has a strong affinity for what the British call "boffins," which roughly translates to "eccentric genius inventors." With a slight resemblance to Doc Brown of "Back to the Future" (as played by Christopher Lloyd), company founder James Dyson epitomizes the type. Now...
While Dyson may be best known worldwide for high-tech vacuum cleaners, the company has a strong affinity for what the British call "boffins," which roughly translates to "eccentric genius inventors." With a slight resemblance to Doc Brown of "Back to the Future" (as played by Christopher Lloyd), company founder James Dyson epitomizes the type. Now...  Dyson, the British appliance company best known for its bagless vacuum cleaners, has cleared up speculation that has persisted for nearly 10 years. Founder and chief engineer James Dyson officially confirmed his company is developing an electric car and is planning for a 2020 launch. Not only has Dyson had 400 employees working on an electric car...
Dyson, the British appliance company best known for its bagless vacuum cleaners, has cleared up speculation that has persisted for nearly 10 years. Founder and chief engineer James Dyson officially confirmed his company is developing an electric car and is planning for a 2020 launch. Not only has Dyson had 400 employees working on an electric car... ![James Dyson with digital motors [image: Dyson]](http://images.hgmsites.net/tmb/james-dyson-with-digital-motors-image-dyson_100531077_t.gif) Just 18 months after its $90m acquisition of Sakti3, the British consumer-products company Dyson is taking a step back. Dyson has chosen to relinquish the patent rights that were the core intellectual property of the Michigan based start-up company. Its move demonstrates the high risk companies are willing to accept in order to be at the forefront...
Just 18 months after its $90m acquisition of Sakti3, the British consumer-products company Dyson is taking a step back. Dyson has chosen to relinquish the patent rights that were the core intellectual property of the Michigan based start-up company. Its move demonstrates the high risk companies are willing to accept in order to be at the forefront... 